Cost price
A designer must know the cost objective and the cost estimate of his or her design.
Approximately 70% of the costs can be influenced at the start of the product design. This cost awareness in the early phase of a design is important to realize a successful product at the desired costs.
- Cost target
The cost target is in most cases defined in the design assignment or design specification. This in turn is a derivative of what the customer is willing to pay.
- Cost estimation
In general, the cost of a product is the sum of the material costs plus assembly labor and profit.
Because at the start of the design process it is difficult to determine the costs, the following definitions are used:
Level 1 parametric: an estimate based on prior experience. A quick and dirty way to look at cost is to figure out the mark-up for an industry.
Level 2 analogy: an estimate based on prior experience with similar product with documented rationale.Usual cost can be roughly calculated in cost per mass, vulome or surface. Sometimes extrapolation at a trundling can be used . (€/ kW, €/kg, €/part … )
Level 3 analytical: a detailed costing calculation.
Also the production volume is influencing the costs to a large extent.
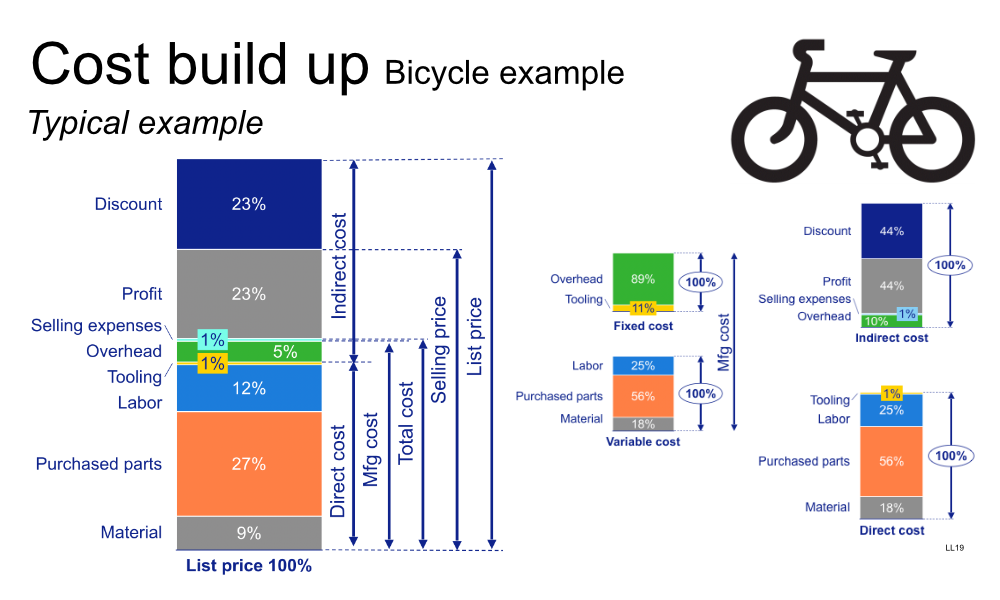
Below an example of a detailed costing model.